Penn State Roadway Asset Management
The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA |
| ||
|
Penn State implemented a roadway maintenance prioritization system to strategically plan roadway maintenance and oversee roadway assets over a 20-year cycle. The project required development of a linear Location Reference System (LRS) for the main campus roadway network and satellite facility networks (approximately 100 miles). A roadway condition survey for each roadway segment was conducted, resulting in a numeric condition index. The condition rating was used in conjunction with a criticality rating, a customized deterioration model, and standard maintenance and repair options to develop an ordered list of maintenance projects.
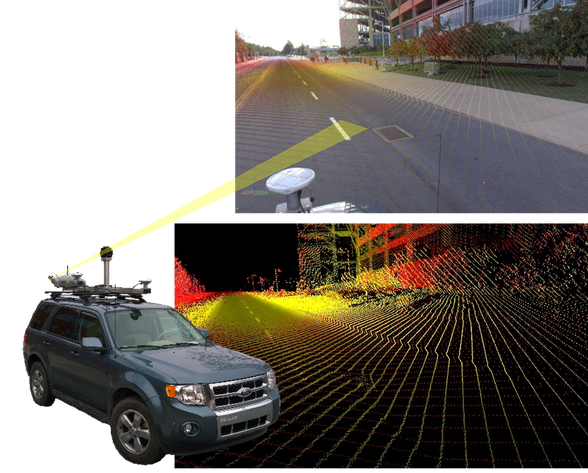
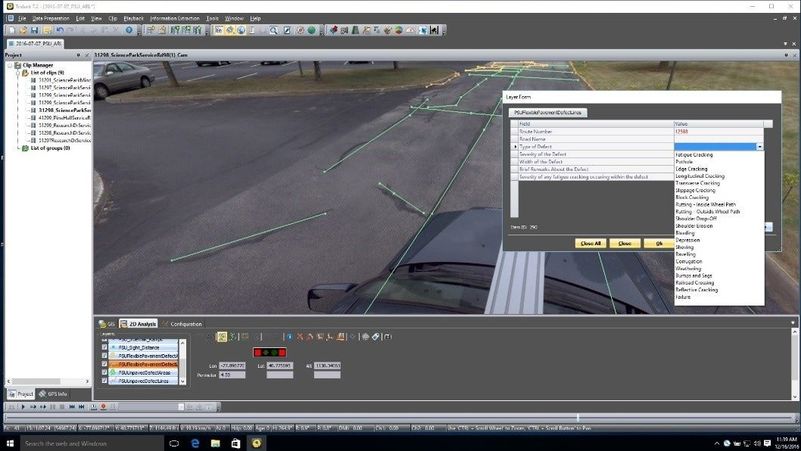
To fully document and archive the condition of the roadway surfaces, Stahl Sheaffer Engineering completed 3D LiDAR scans, georeferenced high-definition videos, and 360° imagery of all 100 miles of Penn State’s roadway networks. The scans and imagery were then used to assess 312 roadway segments, including features and surface deficiency. Among the attributes extracted were curbs, sidewalks, ADA ramps, bus pull-off areas, intersection sight distance sufficiency, and parallel drainage ditches. The information collected and archived for each feature was customized to reflect relevant attributes and numeric condition rating. All features are georeferenced, compatible with Geographic Information Systems (GIS), and easily located by the LRS ID number and station offset.
|
Figure 1: Dropdown Features Used to Classify Roadway Conditions
Documented by LiDAR Scanning |
The tool allows for various funding scenarios to be analyzed. Budgets can be predetermined based on funding availability or calculated based on the need to maintain assets at a certain service level. The versatility of the tool is perfect for managing a maintenance budget and schedule because it can provide useful data according to different scenarios, including:
It can be adjusted to view either scenario or different budget amounts and recalculates automatically according to those inputs as well as completed repairs or date changes to accommodate bundled construction projects.
- Resulting roadway network health over time with repairs that fit into established annual budget, OR
- Budget needed to maintain network in a desired state of health (i.e., 85% PCI or “Good”) over a specified period of time.
It can be adjusted to view either scenario or different budget amounts and recalculates automatically according to those inputs as well as completed repairs or date changes to accommodate bundled construction projects.
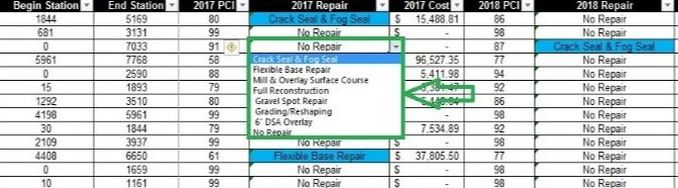
Figure 2: Repair options for each roadway segment can be changed, which will update the priority and budget impacts for the 20-year plan.
The initial project was implemented at University Park and its satellite locations but rolled out to include 258 miles of roadway and approximately 600 parking lots at 23 campuses across the Commonwealth.